Hard Drives
In the world of data storage, SSD and HDD are the two main technologies for storing your files. The difference primarily comes down to moving parts vs. flash memory.
HDD (Hard Disk Drive)
An HDD is the traditional storage technology. It uses physical, spinning magnetic platters and a moving “read/write head” to access data—much like a high-tech record player.
- Pros: Generally cheaper for high capacities (e.g., 8TB or 12TB drives).
- Cons: Slower, noisier, and more fragile because if you drop it while it’s spinning, the physical parts can break.
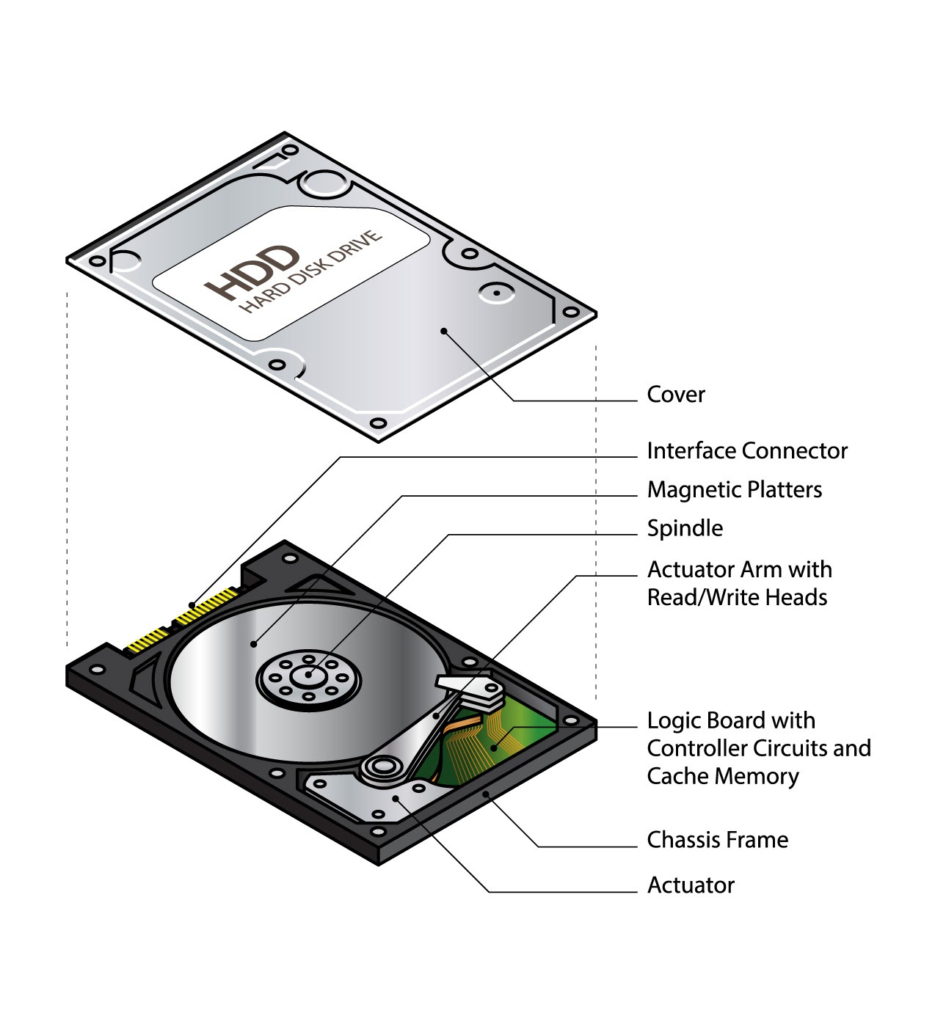
SSD (Solid State Drive)
An SSD is a newer, faster technology that uses “flash” memory—the same kind of tech found in USB thumb drives, but much faster and more reliable. There are no moving parts inside.
- Pros: Incredibly fast boot times, silent operation, and high durability.
- Cons: Generally more expensive per gigabyte than HDDs (though prices are dropping rapidly).
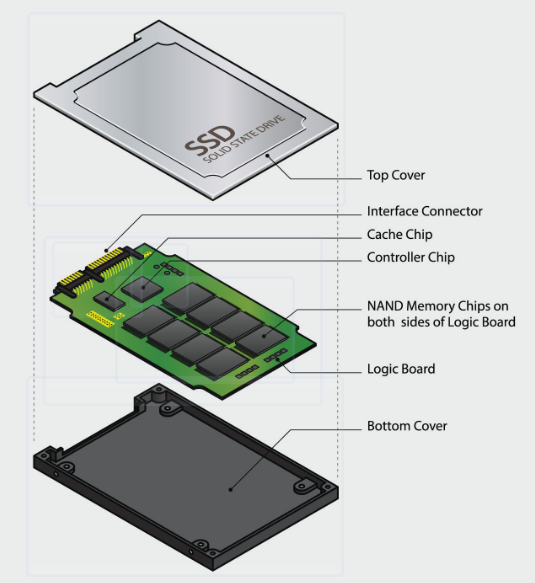
Comparison at a Glance
| Feature | HDD | SSD |
| Speed | Slower (Moving parts take time to find data) | Much faster (Data is accessed instantly) |
| Durability | Vulnerable to physical shock/drops | Highly resistant to drops |
| Lifespan | Mechanical wear over time | Limited “write cycles,” but usually lasts years |
| Best Use Case | Mass storage (Photos, backups, movies) | Operating systems, gaming, and daily tasks |
When it comes to Solid State Drives, the terms SATA and NVMe refer to the “language” and the “pathway” the drive uses to talk to your computer. Even though both are SSDs, the speed difference is massive.
SATA SSDs
SATA (Serial ATA) is an older interface originally designed for those slow, spinning hard drives (HDDs).
- The Bottleneck: Because it was built for older tech, SATA has a speed limit. It’s like a fast car stuck on a narrow residential street with a 35 mph speed limit.
- Speed: Maxes out around 600 MB/s.
- Physical Shape: Usually looks like a small, flat 2.5-inch plastic brick.
NVMe SSDs
NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express) was designed specifically for flash memory. It uses the PCIe lanes in your computer—the same high-speed “highways” used by graphics cards.
- The Breakthrough: It removes the bottlenecks of the old SATA system. It’s like taking that same fast car and putting it on a 10-lane super-highway with no speed limit.
- Speed: Modern NVMe drives can reach 3,500 MB/s to 7,500 MB/s (and even higher with Gen5).
- Physical Shape: Usually looks like a small stick of gum (the M.2 form factor) that plugs directly into the motherboard.
Comparison Summary
| Feature | SATA SSD | NVMe SSD |
| Interface | Legacy (designed for HDDs) | Modern (designed for Flash) |
| Max Speed | ~600 MB/s | Up to 7,500+ MB/s |
| Installation | Requires cables (usually) | Plugs directly into motherboard |
| Best For | Upgrading old PCs, bulk storage | Gaming, video editing, fast boot times |
The Bottom Line: If you are buying a new drive today and your computer supports it, NVMe is the way to go. It is significantly faster for a similar price point.